ISAs are being ”Simplified”
Dominic Thomas
April 2024 • 5 min read
ISAs are being ”Simplified”
I don’t like sounding (or being) cynical (there’s a but coming isn’t there!) … but – when a Government or HMRC use the word “simplification” they seem to merely describe their own thought process and nothing else. The intention is usually good, the real-world working, well … not so much.
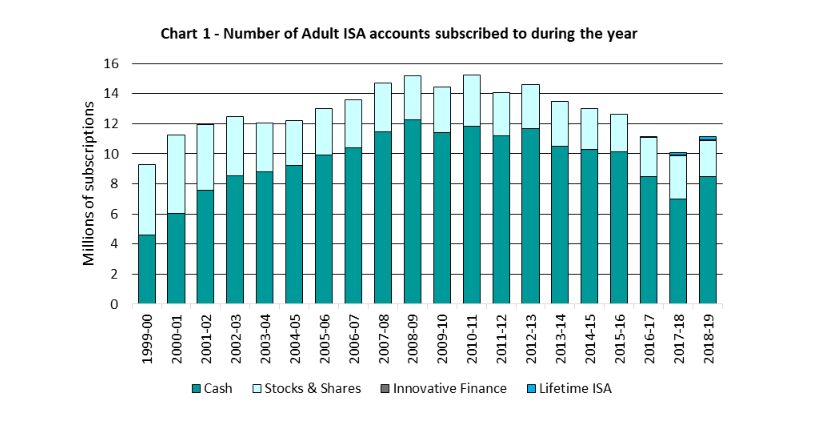
There are some rule changes, announced by the Chancellor in the Autumn statement, that are designed to simplify the scheme and encourage more people to invest tax-free, allowing for a more ‘balanced’ investment portfolio. There are too many ISAs being used as cash deposit accounts by ‘nervous’ investors. Our clients tend not to fall into this trap, but of course millions of people do. Inflation is best beaten over time by investment into assets that grow (holdings in companies listed on the world stock markets). Cash is simply giving banks your money so that they can invest it for their benefit.
Here are the six reforms from HMRC:
The Government announced a package of ISA reforms and will make these changes to ISAs from 6 April 2024:
- Increase the age for opening Cash ISAs from 16 to 18 and over. This is consistent with the age requirement already in place for opening Stocks and Shares, Innovative Finance and Lifetime ISAs.
- Allow subscriptions to multiple ISAs of the same type, with the exception of Lifetime ISA, within the tax year, removing the limit on subscribing to one ISA of each type per year. All subscriptions must remain within the overall ISA limit of £20,000.
- Remove the requirement for an investor to make a fresh ISA application where an existing ISA account has received no subscription in the previous tax year.
- Allow Long-Term Asset Funds to be permitted investments in an Innovative Finance ISA, which does not require access to funds within 30 days.
- Allow open-ended property funds with extended notice periods to be permitted investments in an Innovative Finance ISA.
- Allow partial transfers of current year ISA subscriptions between ISA managers.
The government also plans to hold discussions with industry on allowing certain fractions of shares to become permitted ISA investments.
Most of this will not impact you, everything we do here at Solomon’s is flexible and one of the benefits of regular reviews is that we can assess and check ongoing suitability of the financial products we have arranged for you and the portfolio being used.
If you have any questions at all, please get in touch. If you need a review sooner than normal or feel one may be overdue, please drop us a line.